How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to give a good presentation that captivates any audience

Jump to section
What are the main difficulties when giving presentations?
How to create an effective presentation, after that, how do i give a memorable presentation, how to connect with the audience when presenting.
If you’ve ever heard someone give a powerful presentation, you probably remember how it made you feel. Much like a composer, a good speaker knows precisely when each note should strike to captivate their audience’s attention and leave them with a lasting impression.
No one becomes a great public speaker or presenter without practice. And almost everyone can recall a time one of their presentations went badly — that’s a painful part of the learning process.
Whether you’re working within a small creative team or a large organization, public speaking and presentation skills are vital to communicating your ideas. Knowing how to present your vision can help you pitch concepts to clients, present ideas to your team, and develop the confidence to participate in team meetings.
If you have an upcoming presentation on the horizon and feel nervous, that’s normal. Around 15-30% of the general population experience a fear of public speaking . And, unfortunately, social anxiety is on the rise, with a 12% increase in adults over the last 20 years .
Learning how to give a good presentation can dismantle your fears and break down these barriers, ensuring you’re ready to confidently share your point of view.
It’s the week before your presentation, and you’re already feeling nervous . Maybe there’ll be an important mentor in the room you need to impress, or you’re looking for an opportunity to show your boss your value. Regardless of your countless past presentations, you still feel nervous.
Sharing your vision and ideas with any sized group is intimidating. You’re likely worrying about how you’ll perform as a presenter and whether the audience will be interested in what you offer. But nerves aren’t inherently negative — you can actually use this feeling to fuel your preparation.

It’s helpful to identify where your worries are coming from and address your fears. Here are some common concerns when preparing for an upcoming presentation:
Fear of public speaking: When you share your ideas in front of a group, you’re placing yourself in a vulnerable position to be critiqued on your knowledge and communication skills . Maybe you feel confident in your content, but when you think about standing in front of an audience, you feel anxious and your mind goes blank.
It’s also not uncommon to have physical symptoms when presenting . Some people experience nausea and dizziness as the brain releases adrenaline to cope with the potentially stressful situation . Remember to take deep breaths to recenter yourself and be patient, even if you make a mistake.
Losing the audience’s attention: As a presenter, your main focus is to keep your audience engaged. They should feel like they’re learning valuable information or following a story that will improve them in life or business.
Highlight the most exciting pieces of knowledge and ensure you emphasize those points in your presentation. If you feel passionate about your content, it’s more likely that your audience will experience this excitement for themselves and become invested in what you have to say.
Not knowing what content to place on presentation slides: Overloading presentation slides is a fast way to lose your audience’s attention. Your slides should contain only the main talking points and limited text to ensure your audience focuses on what you have to say rather than becoming distracted by the content on your slides.
Discomfort incorporating nonverbal communication: It’s natural to feel stiff and frozen when you’re nervous. But maintaining effective body language helps your audience stay focused on you as you speak and encourages you to relax.
If you struggle to incorporate body language into your presentations, try starting small by making hand gestures toward your slides. If you’re working with a large audience, use different parts of the stage to ensure everyone feels included.
Each presenter has their own personal brand and style. Some may use humor to break the ice, while others might appeal to the audience’s emotional side through inspiring storytelling.
Watching online presentations, such as TED talks, is an excellent way to expose yourself to various presentation styles and develop your own. While observing others, you can note how they carry themselves on stage and learn new ways to keep your audience engaged.
Once you’ve addressed what’s causing your fears, it’s time to prepare for a great presentation. Use your past experience as inspiration and aim to outshine your former self by learning from your mistakes and employing new techniques. Here are five presentation tips to help you create a strong presentation and wow your audience:
1. Keep it simple
Simple means something different to everyone.
Before creating your presentation, take note of your intended audience and their knowledge level of your subject. You’ll want your content to be easy for your intended audience to follow.
Say you’re giving a presentation on improving your company’s operational structure. Entry-level workers will likely need a more straightforward overview of the content than C-suite leaders, who have significantly more experience.
Ask yourself what you want your audience to take away from your presentation and emphasize those important points. Doing this ensures they remember the most vital information rather than less important supporting ideas. Try organizing these concepts into bullet points so viewers can quickly identify critical takeaways.
2. Create a compelling structure
Put yourself in your audience member’s shoes and determine the most compelling way to organize your information. Your presentation should be articulate , cohesive, and logical, and you must be sure to include all necessary supporting evidence to strengthen your main points.
If you give away all of your answers too quickly, your audience could lose interest. And if there isn’t enough supporting information, they could hit a roadblock of confusion. Try developing a compelling story that leads your audience through your thought processes so they can experience the ups and downs alongside you.
By structuring your presentation to lead up to a final conclusion, you’re more likely to keep listeners’ attention. Once you’ve reached that conclusion, you can offer a Q&A period to put any of their questions or concerns to rest.
3. Use visual aids
Appealing to various learning styles is a great way to keep everyone on the same page and ensure they absorb your content. Visual aids are necessary for visual learners and make it easier for people to picture your ideas.
Aim to incorporate a mixture of photos, videos, and props to engage your audience and convey your key points. For instance, if you’re giving a presentation on anthropology subject matter, you could show your audience an artifact to help them understand how exciting a discovery must have been.
If your presentation is long, including a video for your audience to watch is an excellent way to give yourself a break and create new jumping-off points for your speech.
4. Be aware of design techniques and trends
Thanks to cutting-edge technology and tools, you have numerous platforms at your disposal to create a good presentation. But keep in mind that although color, images, and graphics liven things up, they can cause distraction when misused.
Here are a few standard pointers for incorporating visuals on your slides:
- Don’t place blocks of small text on a single slide
- Use a minimalistic background instead of a busy one
- Ensure text stands out against the background color
- Only use high-resolution photos
- Maintain a consistent font style and size throughout the presentation
- Don’t overuse transitions and effects
5. Try the 10-20-30 rule
Guy Kawasaki, a prominent venture capitalist and one of the original marketing specialists for Apple, said that the best slideshow presentations are less than 10 slides , last at most 20 minutes, and use a font size of 30. Following this strategy can help you condense your information, eliminate unnecessary ideas, and maintain your audience’s focus more efficiently.
Once you’re confident in creating a memorable presentation, it’s time to learn how to give one. Here are some valuable tips for keeping your audience invested during your talk:
Tip #1: Tell stories
Sharing an anecdote from your life can improve your credibility and increase your relatability. And when an audience relates to you, they’re more likely to feel connected to who you are as a person and encouraged to give you their full attention, as they would want others to do the same.
Gill Hicks utilized this strategy well when she shared her powerful story, “ I survived a terrorist attack. Here’s what I learned .” In her harrowing tale, Hicks highlights the importance of compassion, unconditional love , and helping those in need.
If you feel uncomfortable sharing personal stories, that’s okay. You can use examples from famous individuals or create a fictional account to demonstrate your ideas.
Tip #2: Make eye contact with the audience
Maintaining eye contact is less intimidating than it sounds. In fact, you don’t have to look your audience members directly in their eyes — you can focus on their foreheads or noses if that’s easier.
Try making eye contact with as many people as possible for 3–5 seconds each. This timing ensures you don’t look away too quickly, making the audience member feel unimportant, or linger too long, making them feel uncomfortable.
If you’re presenting to a large group, direct your focus to each part of the room to ensure no section of the audience feels ignored.

Tip #3: Work on your stage presence
Although your tone and words are the most impactful part of your presentation, recall that body language keeps your audience engaged. Use these tips to master a professional stage presence:
- Speak with open arms and avoid crossing them
- Keep a reasonable pace and try not to stand still
- Use hand gestures to highlight important information
Tip #4: Start strong
Like watching a movie trailer, the first seconds of your talk are critical for capturing your audience’s attention. How you start your speech sets the tone for the rest of your presentation and tells your audience whether or not they should pay attention. Here are some ways to start your presentation to leave a lasting impression:
- Use a quote from a well-known and likable influential person
- Ask a rhetorical question to create intrigue
- Start with an anecdote to add context to your talk
- Spark your audience’s curiosity by involving them in an interactive problem-solving puzzle or riddle
Tip #5: Show your passion
Don’t be afraid of being too enthusiastic. Everyone appreciates a speaker who’s genuinely excited about their field of expertise.
In “ Grit: The Power of Passion and Perseverance ,” Angela Lee Duckworth discusses the importance of passion in research and delivery. She delivers her presentation excitedly to show the audience how excitement piques interest.
Tip #6: Plan your delivery
How you decide to deliver your speech will shape your presentation. Will you be preparing a PowerPoint presentation and using a teleprompter? Or are you working within the constraints of the digital world and presenting over Zoom?
The best presentations are conducted by speakers who know their stuff and memorize their content. However, if you find this challenging, try creating notes to use as a safety net in case you lose track.
If you’re presenting online, you can keep notes beside your computer for each slide, highlighting your key points. This ensures you include all the necessary information and follow a logical order.

Tip #7: Practice
Practice doesn’t make perfect — it makes progress. There’s no way of preparing for unforeseen circumstances, but thorough practice means you’ve done everything you can to succeed.
Rehearse your speech in front of a mirror or to a trusted friend or family member. Take any feedback and use it as an opportunity to fine-tune your speech. But remember: who you practice your presentation in front of may differ from your intended audience. Consider their opinions through the lens of them occupying this different position.
Tip #8: Read the room
Whether you’re a keynote speaker at an event or presenting to a small group of clients, knowing how to read the room is vital for keeping your audience happy. Stay flexible and be willing to move on from topics quickly if your listeners are uninterested or displeased with a particular part of your speech.
Tip #9: Breathe
Try taking deep breaths before your presentation to calm your nerves. If you feel rushed, you’re more likely to feel nervous and stumble on your words.
The most important thing to consider when presenting is your audience’s feelings. When you approach your next presentation calmly, you’ll put your audience at ease and encourage them to feel comfortable in your presence.
Tip #10: Provide a call-to-action
When you end your presentation, your audience should feel compelled to take a specific action, whether that’s changing their habits or contacting you for your services.
If you’re presenting to clients, create a handout with key points and contact information so they can get in touch. You should provide your LinkedIn information, email address, and phone number so they have a variety of ways to reach you.
There’s no one-size-fits-all template for an effective presentation, as your unique audience and subject matter play a role in shaping your speech. As a general rule, though, you should aim to connect with your audience through passion and excitement. Use strong eye contact and body language. Capture their interest through storytelling and their trust through relatability.
Learning how to give a good presentation can feel overwhelming — but remember, practice makes progress. Rehearse your presentation for someone you trust, collect their feedback , and revise. Practicing your presentation skills is helpful for any job, and every challenge is a chance to grow.
Enhance your presentation skills
Discover coaching that transforms your public speaking and boosts your confidence in presenting.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
6 presentation skills and how to improve them
3 stand-out professional bio examples to inspire your own, tell a story they can't ignore these 10 tips will teach you how, reading the room gives you an edge — no matter who you're talking to, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, the importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, fear of public speaking overcome it with these 7 tips, how to not be nervous for a presentation — 13 tips that work (really), what is a stipend how it works and tips to make the most of it, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
- Presentations
- Most Recent
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Design for Business
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Start a Presentation: 12 Ways to Keep Your Audience Hooked

Written by: Nayomi Chibana

Wondering how to start a presentation that makes your audience sit up in their seats with excitement?
"Today, you will learn something that will add 10 years to your life."
"20 years from now, your job won't exist."
"Did you know that more people have access to a mobile phone than a toilet?"
Presentation starters like these are key to grabbing your audience's attention and making the most of the time allotted to you.
Instead of thanking the audience, making an unrelated joke or apologizing for a technical issue, why not dive right into the subject matter with a gripping statement or thought-provoking question?
To help you craft your own killer presentation starters, we've sorted through some of the most popular TED talks in history and created this list of the most effective ways to start your next presentation .
Many of these presentation starters are successful because they appeal to human emotions such as curiosity, awe, surprise or fear. You can read more on creating viral content that triggers emotional responses in this post .
Better yet, check out the video version of this blog post. This video distills 12 killer strategies to start your presentation and keep the audience's attention throughout.

- Knowing how to start a presentation is crucial because it sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. A strong and engaging opening can capture the audience's attention and generate interest in your presentation.
- There are many ways to start a presentation: make a provocative statement, incite curiosity; shock the audience; tell a story, be authentic; quote a famous or influential person.
- Here are other presentation opening strategies: Begin with a captivating visual; ask a question; use silence; start with a prop; tell a relevant joke; use the word "imagine.
- Take advantage of Visme's free online presentation software to create attention-grabbing presentations that align with your branding and engage your audience.
- If you're short on time, tap into the power of Visme's AI presentation maker to create stunning presentations in minutes. Simply describe what you want to create, select your preferred design option and let the tool do the heavy lifting.
How to Start a Presentation
Knowing how to start a presentation is just as crucial as the message you're trying to convey. If you can't start it effectively, you might not be able to leave a strong enough impact by the end of it.
TED speakers are some of the best presenters in the world, and there's a lot you can learn from their talks. Below, we've handpicked some of these presentations that start with a bang and manage to keep the audience hooked till the very end.
1 Make a provocative statement.
"I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you're going to fail to have a great career."
One surefire way to get your audience's attention is to make a provocative statement that creates interest and a keen desire to know more about what you have to say.
The presentation above, for example, does just that by making a surprising first statement that inspires surprise, amusement, curiosity and fear at the same time.
With 4.8 million views and counting, this talk by an economics professor draws you in precisely because it steers clear of the traditional talk, using blunt humor to enumerate all the irrational excuses people make for not pursuing their dreams and passions.
2 Incite curiosity.
"I need to make a confession at the outset here. A little over 20 years ago, I did something that I regret, something that I'm not particularly proud of. Something that, in many ways, I wish no one would ever know, but here I feel kind of obliged to reveal."
Another way to grab your audience by the collar is to incite curiosity. In this popular TED talk viewed over 15.4 million times, career analyst Dan Pink succeeds at getting the entire audience to look at him intently, waiting for his next word, by resorting to an opening statement that builds suspense.
Since human beings are by nature curious creatures, most people in the audience were probably asking themselves "What did he do?" and imagining all sorts of possible scenarios.
3 Shock the audience.
"You will live seven and a half minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk."
In many ways related to the previous two presentation starters, this hook involves making a counter-intuitive or paradigm-shifting statement that goes against a popular belief or simply shocks due to the perceived impossibility of the proposed statement.
This introduction by game designer Jane McGonigal, for example, achieves a level of surprise by making a seemingly improbable assertion. After hearing this kind of statement, most people will want to listen to your entire talk, if not out of genuine interest, then at least for the sake of pacifying their incredulity.
(By the way, she makes good on her promise by revealing a game she designed to boost resilience, which is backed by scientific research.)
4 Tell a story.
"When I was seven years old and my sister was just five years old, we were playing on top of a bunk bed..."
As covered in a previous post , storytelling is the key ingredient that separates good, engaging presentations from bad ones that lack a clear message and persuasive delivery.
In his popular talk on the secret to being more productive, psychologist Shawn Achor tells a childhood story to lead into the effectiveness of positive psychology. He then goes on to provide concrete evidence backing his claim that pursuing happiness, rather than productivity for its own sake, actually makes you more--not less--productive.
Create a stunning presentation in less time
- Hundreds of premade slides available
- Add animation and interactivity to your slides
- Choose from various presentation options
Sign up. It’s free.

5 Be authentic.
"I'm going to tell you a little bit about my TEDxHouston Talk. I woke up the morning after I gave that talk with the worst vulnerability hangover of my life. And I actually didn't leave my house for about three days."
Another way to draw your audience into your own world is to tell a revealing personal story. This is certainly not easy but, when done right, can quickly spark interest in your topic and build an emotional connection between you and your audience.
In Brene Brown's talk on confronting shame, she begins by admitting that she felt embarrassed over the revelations she had made in her massively popular TED talk on embracing vulnerability.
6 Quote an influential person.
One of the easiest ways to start a presentation is to quote an influential person. In these cases, it's best to use a pithy, short and relevant quote to catch your audience's attention.
In the widely viewed video above, for example, writer Andrew Solomon quotes Emily Dickinson to begin his talk on depression, an illness he asserts affects many more people than the official figures suggest.
The quote is particularly powerful and effective because it eloquently describes the state of depression from the point of view of a person who is feeling all the emotions associated with it.
7 Begin with a captivating visual.
To introduce this fascinating TED talk on how movements really get started, entrepreneur Derek Sivers uses some surprising footage to support his statements. They are especially captivating because they debunk widely held beliefs on the matter, proving that it takes more than just a charismatic leader to start a revolution of any sort.
8 Ask a question.
"Do you think it's possible to control someone's attention? Even more than that, what about predicting human behavior?"
In this attention-grabbing presentation on the flaws in human perception, world-famous pickpocket Apollo Robbins starts off by asking the audience a question that leads right into the meat of his talk, which has been viewed worldwide more than 10.5 million times.
In these cases, it's best to pose a question that will really get your audience thinking and, in the best possible scenario, challenge their prevailing beliefs or preconceptions on a certain topic.
51 Best Presentation Slides for Engaging Presentations (2024)
9 Use silence.
Another effective technique--which should only be used if you're a seasoned presenter and are able to maintain your composure throughout--is to leverage silence to command a room.
Watch, for example, how musician Amanda Palmer starts off her talk by not saying a word, simply breathing in and out and using props to communicate her message.
Although you may not want to resort to both silence and using a prop in your presentation, this is a very effective dramatic technique that, if done right, quickly draws all eyes to you.
10 Start with a prop.
Considering that the audience's gaze is attracted by motion and visual objects, another way to hook them right from the outset is to use a prop.
Take a look at how best-selling author Susan Cain uses a physical object to visually complement her opening story on her first summer camp experience. It not only adds a dramatic effect, it also keeps viewers eyes on her while on stage.
11 Tell a relevant joke.
"Okay, now I don't want to alarm anybody in this room, but it's just come to my attention that the person to your right is a liar."
Humor is not only a good way to break the ice and endear the audience to you right from the outset, it can also be very effective in getting your point across if it's relevant to your talk.
Lie detector Pamela Meyer, for example, deftly uses both humor and an element of surprise in her opening statement as she tells the audience that the person to their right is probably a liar. This gets the audience to laugh and then focus on her topic at the same time.
She goes on to give some shocking statistics (such as that on any given day, we're lied to up to 200 times) and delivers an intriguing talk that has been seen close to 13 million times.
12 Use the word "imagine."
"Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary."
Lastly, there are times when leading your audience to use their imaginations is the best bet. You can prompt them to do this by using the commands "imagine," "think of" or "picture this." These are just a few of the most powerful opening words for presentation.
Plane crash survivor Ric Elias, for example, uses this technique in the video above to quickly thrust his audience into the central scene of his harrowing story.
Learn How to Start a Presentation Effectively
What about your next presentation? Have you thought about how you're going to set the mood for your talk? We've rounded up some of the best way to start a presentation.
When you're ready to get started creating your presentation, give Visme's presentation software a try! The tool comes with an AI writer that helps you generate killer content for your next presentation in seconds.
Plus, check out our post on how to end a presentation so you both start and end your speech with a bang.
And if you want to learn all our secrets on how to deliver an unforgettable presentation, as well as how to create visual slides with impact, grab our free e-book below.

Create beautiful presentations faster with Visme.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Nayomi Chibana is a journalist and writer for Visme’s Visual Learning Center. Besides researching trends in visual communication and next-generation storytelling, she’s passionate about data-driven content.
- Alternatives
How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 April, 2024 • 9 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You're standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we'll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let's dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
| How long does it take to make a presentation? | 20 - 60 hours. |
| How can I improve my presentation writing? | Minimize text, optimize visuals, and one idea per slide. |
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you've got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience's attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?"
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?"
- Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...."
- Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...."
- Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: "In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,... Next,... Finally,.... we'll discuss...."
- Provide Background and Context: Example: "Before we dive into the details, let's understand the basics of....."
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: "To illustrate...., let's look at an example. In,....."
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: "While..., we must also consider... ."
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: "To summarize, we've... Now, let's shift our focus to..."
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: "As we conclude our presentation, it's clear that... By...., we can...."
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you've outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: "As you can see from this graph,... This demonstrates...."
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it's crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation - the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience's attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience's attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience's attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
"Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that's exactly what we'll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it's vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we'll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let's get started!"
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you're a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation's impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let's take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?" Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?" Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...." Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...." Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience's attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 15 May 2019
Ways to give an effective seminar about your research project
- Ananya Sen 0
Ananya Sen is a PhD student in microbiology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
In my first year of graduate school, I was terrified of giving presentations. I would put too much information on my slides, talk too fast and constantly forget or trip over certain words. Unsuprisingly, the reception was lukewarm at best.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01574-z
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged. You can get in touch with the editor at [email protected].
Related Articles

- Communication
- Conferences and meetings

‘All things that wander in the heavens’: how I swapped my ivory tower for the world of science fiction
Career Q&A 04 JUL 24

How researchers and their managers can build an actionable career-development plan
Career Column 17 JUN 24

Securing your science: the researcher’s guide to financial management
Career Feature 14 JUN 24

Hybrid conferences should be the norm — optimize them so everyone benefits
Editorial 06 AUG 24

How to spot a predatory conference, and what science needs to do about them: a guide
Career Feature 30 JUL 24

Predatory conferences are on the rise. Here are five ways to tackle them
Editorial 30 JUL 24

Slow productivity worked for Marie Curie — here’s why you should adopt it, too
Career Feature 05 AUG 24

Quantum computing aims for diversity, one qubit at a time
Technology Feature 05 AUG 24
Open Faculty Positions at the State Key Laboratory of Brain Cognition & Brain-inspired Intelligence
The laboratory focuses on understanding the mechanisms of brain intelligence and developing the theory and techniques of brain-inspired intelligence.
Shanghai, China
CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT)
Postdoctoral Associate- Molecular Biology and Cancer Immunotherapy
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Editor, BMC Medicine
As Editor at BMC Medicine, you will handle original research papers, commission content and travel internationally to promote the journal.
London, Beijing or Shanghai – Hybrid Working Model
Springer Nature Ltd
Assistant Professor (Tenure Track) of Biopharmaceutical Systems & Pharmacokinetics
The Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences at ETH Zurich (www.chab.ethz.ch) invites applications for the above-mentioned position.
Zurich, Switzerland
Postdoctoral Researcher
National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) invites applications for postdoctoral researchers. . For more details, please visit the URL bel...
Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan (JP)
National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

6 Tips For Giving a Fabulous Academic Presentation
6-tips-for-giving-a-fabulous-academic-presentation.
Tanya Golash-Boza, Associate Professor of Sociology, University of California
January 11, 2022
One of the easiest ways to stand out at an academic conference is to give a fantastic presentation.
In this post, I will discuss a few simple techniques that can make your presentation stand out. Although, it does take time to make a good presentation, it is well worth the investment.
Tip #1: Use PowerPoint Judiciously
Images are powerful. Research shows that images help with memory and learning. Use this to your advantage by finding and using images that help you make your point. One trick I have learned is that you can use images that have blank space in them and you can put words in those images.
Here is one such example from a presentation I gave about immigration law enforcement.
PowerPoint is a great tool, so long as you use it effectively. Generally, this means using lots of visuals and relatively few words. Never use less than 24-point font. And, please, never put your presentation on the slides and read from the slides.
Tip #2: There is a formula to academic presentations. Use it.
Once you have become an expert at giving fabulous presentations, you can deviate from the formula. However, if you are new to presenting, you might want to follow it. This will vary slightly by field, however, I will give an example from my field – sociology – to give you an idea as to what the format should look like:
- Introduction/Overview/Hook
- Theoretical Framework/Research Question
- Methodology/Case Selection
- Background/Literature Review
- Discussion of Data/Results
Tip #3: The audience wants to hear about your research. Tell them.
One of the most common mistakes I see in people giving presentations is that they present only information I already know. This usually happens when they spend nearly all of the presentation going over the existing literature and giving background information on their particular case. You need only to discuss the literature with which you are directly engaging and contributing. Your background information should only include what is absolutely necessary. If you are giving a 15-minute presentation, by the 6 th minute, you need to be discussing your data or case study. At conferences, people are there to learn about your new and exciting research, not to hear a summary of old work.
Tip #4: Practice. Practice. Practice.
You should always practice your presentation in full before you deliver it. You might feel silly delivering your presentation to your cat or your toddler, but you need to do it and do it again. You need to practice to ensure that your presentation fits within the time parameters. Practicing also makes it flow better. You can’t practice too many times.
Tip #5: Keep To Your Time Limit
If you have ten minutes to present, prepare ten minutes of material. No more. Even if you only have seven minutes, you need to finish within the allotted time. If you write your presentation out, a general rule of thumb is two minutes per typed, double-spaced page. For a fifteen-minute talk, you should have no more than 7 double-spaced pages of material.
Tip #6: Don’t Read Your Presentation
Yes, I know that in some fields reading is the norm. But, can you honestly say that you find yourself engaged when listening to someone read their conference presentation? If you absolutely must read, I suggest you read in such a way that no one in the audience can tell you are reading. I have seen people do this successfully, and you can do it too if you write in a conversational tone, practice several times, and read your paper with emotion, conviction, and variation in tone.
What tips do you have for presenters? What is one of the best presentations you have seen? What made it so fantastic? Let us know in the comments below.
Want to learn more about the publishing process? The Wiley Researcher Academy is an online author training program designed to help researchers develop the skills and knowledge needed to be able to publish successfully. Learn more about Wiley Researcher Academy .
Image credit: Tanya Golash-Boza
Read the Mandarin version here .

Watch our Webinar to help you get published
Please enter your Email Address
Please enter valid email address
Please Enter your First Name
Please enter your Last Name
Please enter your Questions or Comments.
Please enter the Privacy
Please enter the Terms & Conditions

Leveraging user research to improve author guidelines at the Council of Science Editors Annual Meeting

How research content supports academic integrity

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for Success

Software to Improve Reliability of Research Image Data: Wiley, Lumina, and Researchers at Harvard Medical School Work Together on Solutions

Driving Research Outcomes: Wiley Partners with CiteAb

ISBN, ISSN, DOI: what they are and how to find them

Image Collections for Medical Practitioners with TDS Health

How do you Discover Content?

Writing for Publication for Nurses (Mandarin Edition)

Get Published - Your How to Webinar
Related articles.
User Experience (UX) Research is the process of discovering and understanding user requirements, motivations, and behaviours
Learn how Wiley partners with plagiarism detection services to support academic integrity around the world
Medical student Nicole Foley shares her top tips for writing and getting your work published.
Wiley and Lumina are working together to support the efforts of researchers at Harvard Medical School to develop and test new machine learning tools and artificial intelligence (AI) software that can
Learn more about our relationship with a company that helps scientists identify the right products to use in their research
What is ISBN? ISSN? DOI? Learn about some of the unique identifiers for book and journal content.
Learn how medical practitioners can easily access and search visual assets from our article portfolio
Explore free-to-use services that can help you discover new content
Watch this webinar to help you learn how to get published.

Finding time to publish as a medical student: 6 tips for success

How to Easily Access the Most Relevant Research: A Q&A With the Creator of Scitrus
Atypon launches Scitrus, a personalized web app that allows users to create a customized feed of the latest research.
FOR INDIVIDUALS
FOR INSTITUTIONS & BUSINESSES
WILEY NETWORK
ABOUT WILEY
Corporate Responsibility
Corporate Governance
Leadership Team
Cookie Preferences
Copyright @ 2000-2024 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., or related companies. All rights reserved, including rights for text and data mining and training of artificial technologies or similar technologies.
Rights & Permissions
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use

Making a short presentation based on your research: 11 tips
Markus goldstein, david evans.
Over the past few weeks, we’ve both spent a fair amount of time at conferences. Given that many conferences ask researchers to summarize their work in 15 to 20 minutes, we thought we’d reflect on some ideas for how to do this, and – more importantly – how to do it well.
- You have 15 minutes. That’s not enough time to use the slides you used for that recent 90-minute academic seminar. One recent presentation one of us saw had 52 slides for 15 minutes. No amount of speed talking will get you through this in anything resembling coherence. (And quit speed talking, anyway. This isn’t a FedEx commercial !) There is no magic number of slides since the content you’ll have and how you talk will vary. But if you have more than 15 slides, then #2 is doubly important.
- Practice. This is the great thing about a 15-minute talk: You can actually afford to run through it, out loud. Running through it once in advance can reveal to you – wow! – that it’s actually a 25-minute talk and you need to cut a bunch. Of course, the first time through the presentation it may take a bit longer than you will when you present, but if you have any doubts, practice again (bringing your prep time to a whopping 30 minutes plus a little bit).
- You need a (short) narrative. What is the main story you are trying to tell with this paper? Fifteen minutes works better for communicating a narrative then for taking an audience through every twist and turn of your econometric grandeur. Deciding on your narrative will help with the discipline in the points that follow.
- A model or results? Even if your audience is all academics, you don’t have academic seminar time. So the first thing to do is to figure out which is more important to get across – your model or your empirical results. Then trim the other one down to one slide, max. If the results are your focus (usually the case for us), give the audience a sense of how the model is set up, and what the main implications are as they pertain to the results you will show. Conversely, if it’s the model that’s more important, the empirical results will come later and you can just give the very brief highlights that bolster the key points.
- The literature. Really, really minimal. If you do it at all, choose only the papers that you are either going to build on in a major way or contradict. For some types of discussants, it may help to include them, even if they don’t meet the other criteria. Marc Bellemare takes an even stronger stance: “Never, ever have a literature review in your slides. If literature reviews are boring to read in papers, they are insanely boring to listen to during presentations.”
- Program details. Here it’s a bit of a balance. The audience needs a flavor for the program, they need to understand what it did and how it’s different from other things (particularly other things with some kinds of evidence). But only in exceptional cases (as in, it’s a really different program for theoretical reasons, or you don’t have more than process results yet) do you want this to eat up a lot of your time.
- You don’t have time to go through the nitty gritty of the data. We get that every detail about the survey was fascinating (we spend a lot of our lives thinking about this). But if it’s not key to the story, save it for a longer presentation (or another paper). And if you’re doing a primarily theoretical paper, this is a bullet on one slide.
- Balance and summary stats. Key summary stats that tell the audience who the people are might make the cut, but 3 slides of every variable that you’ll use are going to be slides you either rip through (telling the audience nothing) or waste most of your time on. Summarize the summary stats. On balance tests: you are either balanced or not. If you are, this gets a bullet at most (you can also just say that). If you’re not, tell us what’s up and why we should or should not worry.
- Pre-analysis plan. If you had it, mention it (quickly). If not, don’t. It’s not critical here.
- A picture may be worth 1,000 numbers. Sometimes, taking that really packed table which is currently in 12 point font and turning it into a graph is going to help you with self-control and help your audience with comprehension. Put the significant results in a bar chart, and use asterisks to tell folks which are significant.
- A special warning about presenting your job market paper. When I (Markus) submitted my job market paper to a journal, the referee report came back noting that this was surely a job market paper since it had 40(!) tables. Key example of how everything matters when you just spent four years of your life collecting each observation. Discipline. You have (or will have) an elevator pitch from the job market – use this to trim your presentation.
- Marc Bellemare has a great series of “22 tips for conference and seminar presentations,” many of which apply to short presentations: “Always provide a preview of your results. This isn’t a murder mystery: it’s only when people know where you’re taking them that they can enjoy the scenery along the way.”
- Jeff Leek has a great guide to giving presentations of different lengths, and what your goal should be: “As a scientist, it is hard to accept that the primary purpose of a talk is advertising, not science.” This is doubly true for a 15-minute talk.
- The AEA Committee on the Status of Women in the Economics Profession has a top 10 list. “Never cut and paste a table from your paper onto a slide. These tables are never easy to read and only irritate your audience. Instead, choose a few results that you want to highlight and present them on a slide in no smaller than 28 font.” We’ve pretty much all done this. It’s bad practice. (“I’m sorry you can’t read this table.” “Oh really, then why did you cut and paste that giant table from your paper into the presentation?!”)
- I (Dave) go back and re-read Jesse Shapiro’s guide on “ How to Give an Applied Micro Talk ” from time to time. It’s more geared toward a full-length seminar, but the advice is so good I can’t resist plugging it here.
Get updates from Development Impact
Thank you for choosing to be part of the Development Impact community!
Your subscription is now active. The latest blog posts and blog-related announcements will be delivered directly to your email inbox. You may unsubscribe at any time.

Lead Economist, Africa Gender Innovation Lab and Chief Economists Office

Senior Fellow, Center for Global Development
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
- Program Design
- Peer Mentors
- Excelling in Graduate School
- Oral Communication
- Written communication
- About Climb
Creating a 10-15 Minute Scientific Presentation
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation
Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions
Two additional videos should prove useful:
Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation walks you through the key principles in designing powerful, easy to read slides.
Delivering a Presentation provides tips and approaches to help you put your best foot forward when you stand up in front of a group.
Other resources include:
Quick Links
Northwestern bioscience programs.
- Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Chemical and Biological Engineering (ChBE)
- Driskill Graduate Program in the Life Sciences (DGP)
- Interdepartmental Biological Sciences (IBiS)
- Northwestern University Interdepartmental Neuroscience (NUIN)
- Campus Emergency Information
- Contact Northwestern University
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- University Policies
- Northwestern Home
- Northwestern Calendar: PlanIt Purple
- Northwestern Search
Chicago: 420 East Superior Street, Rubloff 6-644, Chicago, IL 60611 312-503-8286
- Curriculum Vitae
- DEI Statement
- Doing Economics
- Graduate Student Supervision
- Metrics Mondays
- Suggested Reading
Agricultural and Applied Economics—Without Apology
22 Tips for Conference and Seminar Presentations
Last updated on May 24, 2015
A graduate student whose (excellent) second-year paper was accepted at a few conferences came to my office last week to ask me how she should prepare her conference presentations. Because I have never given much thought to how I actually do prepare for conference and seminar presentations, I told her I would write a blog post on the topic after thinking about it. So here is my list of tips on how to prepare conference and seminar presentations, in no particular order. I’m sure I’m forgetting many things; please feel free to include your own best tips in the comments section.
(Note: If you are doing theory or your presentation contains some theory, I also suggest reading William Thomson’s A Guide for the Young Economist , which offers good if dated advice for budding economic theorists.)
- Whatever you do, make sure you know exactly how long you will have to present, and prepare accordingly. There is nothing worse than showing up for a talk expecting to have the usual 75 minutes only to learn that the norm at that institution is to have a 45-minute talk followed by a 15-minute Q&A. In this case, I think the old rule of thumb of one slide per minute applies. Though this does not mean that a 75-minute seminar needs 75 slides (most of my seminar presentations have fewer than 60 slides), it really does mean that a 15-minute conference presentation should have no more than 15 slides.
- What your presentation should include is really a function of time. For example, when presenting my work with Tara Steinmetz and Lindsey Novak on female genital mutilation (FGM) in a seminar, I go into how there are four types of FGM, present a diagram that shows the area excised under each type and what each type looks after healing, I discuss the physiological and psychological consequences of FGM in depth, etc. But when I presented at the CSAE conference last month , where presenters only have 15 minutes, earlier this month, my motivations occupied three slides, and were essentially “FGM affects 100 million women worldwide and has really bad consequences on their health; trust me on that, okay?” (though I still had five intro slides …) In other words, the less time you have, the more your motivations should be highly concentrated and the quicker they should answer the “Why should we care?” question.
- Should you practice your talk? Absolutely. Practice over and over, and time yourself. The more you advance in your career, the less you’ll have to practice your talks, but as a beginner, you have every interest in practicing under a time constraint. As I mentioned when giving advice on the job market, I never practice my talks and I have done reasonably well following this foolhardy strategy, but this does not mean you should be equally foolhardy.
- One thing graduate students consistently get wrong in presentations is the level of technique. Sure, you just spent the last few years doing almost nothing but learning highly mathematical concepts and methods, and you want to show off, Don’t . At an economics conference, most of your audience will have been there and done that, and your display of technical ability impresses no one, really. You can never go wrong assuming you are presenting to an audience of smart college graduates with no experience in your field. This means you should emphasize the motivations and intuition, and define technical concepts in plain English.
- Inevitably, you’ll have to get technical and lose some people when you present your theory or empirical framework or identification strategy. That’s okay, as long as you bring them back at the end in your conclusions, and as long as you try to explain your theory, empirical framework, or identification in plain English as you go through your more technical slides.
- Always have an outline slide, unless you use a Beamer theme that shows the outline on top and highlights which section you’re in, as in this case. It comforts your audience in that they know where you are taking them with this presentation.
- On a related note, always provide a preview of your results. This isn’t a murder mystery: it’s only when people know where you’re taking them that they can enjoy the scenery along the way.
- I am a big fan of using LaTex and Beamer for presentations. Almost every computer in the world can read .pdf documents and has working “Ctrl” and “L” keys. PowerPoint, however, will sometimes crash on you, or it will not display on a PC the equations that looked so pretty on your Mac, and among economists, I suspect Prezi is interpreted as a sufficient statistic for one’s lack of content. Plus, LaTex does math beautifully. PowerPoint does it horribly not so much.
- For your introduction, use Keith Head’s introduction formula : Hook (titillate your audience with a strong start or broad motivation), Research Question , Antecedents (the four or five studies closest to yours), Value Added (what you are bringing to the table relative to those previous studies), and Roadmap (which is really your outline slide).
- Never, ever have a literature review in your slides. If literature reviews are boring to read in papers, they are insanely boring to listen to during presentations.
- After your introduction, present your theoretical framework, empirical framework, data, results, limitations, and conclusion. Again, depending on how much time you have, you might want to maintain some of those steps to a minimum. One trick that few people seem to know about when presenting is the Magic Appendix Trick: You can have 15 slides for your conference presentation, followed by 30 appendix (i.e., not part of the main attraction) slides which you can resort to if people ask to see them. This is a good place to put descriptive statistics, robustness checks, proofs of propositions, additional graphs, etc.
- If you have a theoretical model in the context of an empirical paper, unless your theory is your main contribution, it might be sufficient to just present your assumptions and testable predictions, and have your full-blown model in your appendix.
- As above, so below, and so your presentation should follow the order in which you discuss things in your paper. It’s also perfectly fine to self-plagiarize here and cut and paste whole sentences from your paper. Writing is rewriting, and hopefully by now your paper is beautifully written. There is no use reinventing the wheel at this stage.
- If you can tell your story with a graph or picture, do so. My two papers which were the most successful in seminars are my aforementioned paper on FGM with Steinmetz and Novak and my forthcoming paper on food prices and food riots. In both cases, the paper contains a graph that essentially tells you the whole story in one simple, self-explanatory picture. Even when presenting to the smartest people in the world, a picture is really worth a thousand words.
- Tables of empirical results should focus on your coefficient(s) of interest. This means that you should have a line in there that says “Control Variables? Yes” for those cases where you do include controls, “Village Fixed Effects? Yes” for those cases where you do include village fixed effects, and so on. Again, stick the full-blown results in the appendix, and present only the results that are the most relevant for your talk as part of the main attraction. See slides 22 to 24 of my CSAE presentation .
- Do not read your slides. Do not learn them by heart. Keep the tone of your presentation conversational. Abstain from making jokes: as a grad student, you want to signal that you have competently investigated an important question and provided a technically sound answer to it. Keep your jokes for when you are a senior scholar in your field.
- Development students: Though you are undoubtedly proud of the fact that you’ve done fieldwork, but unless a picture you took while in the field is absolutely necessary for your audience to understand a point you’re making, avoid fieldwork pictures in your presentations (doubly so for pictures with smiling developing-country children, which are incredibly cliché…)
- Likewise, maps have become pervasive in econ talks these past few years. If you are exploiting some spatial source of variation, go ahead and include a map. But if you’re just including a map because you think your audience won’t know where The Gambia is, put it in the appendix.
- Similarly, I always thought it was a bit odd when people added a last, one-word slide that either said “Questions?” or “Thank You!” Audiences are generally not shy about asking questions, and when they are, they’ll find you after you’re done. As for thanking people, I find that the best thing you can do is thank people for their time and attention either at the beginning or at the end of your presentation.
- I have never had to present a poster at a conference, but here is a list of tips that strike me as sensible. Perhaps the smartest idea for posters is to print your poster on location: since most conferences are held in college towns, you’ll easily find a copy shop where you can print your poster. That way, you will avoid having to travel with your poster, and risking your poster case getting crushed by that inevitable guy on your flight who tries to jam-pack his enormous-size “carry-on” luggage in the overhead compartment by pushing as hard as he can on everything else inside.
- When questions arise, answer them to the best of your ability. If you don’t know, say that you don’t know. If your answer is tentative, explain that your answer is off the top of your head. If a question is obviously of little interest to most people, or takes you too far afield, politely offer to discuss it with the person who asked after the talk.
- Above all, have fun. Giving talks is the most effective way to communicate your excitement about your research. If you are not having fun, chances are people in the audience aren’t either, and if they aren’t having fun, they cannot get excited about your research, which means that your impact will be much more limited.
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Published in Uncategorized

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research

How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
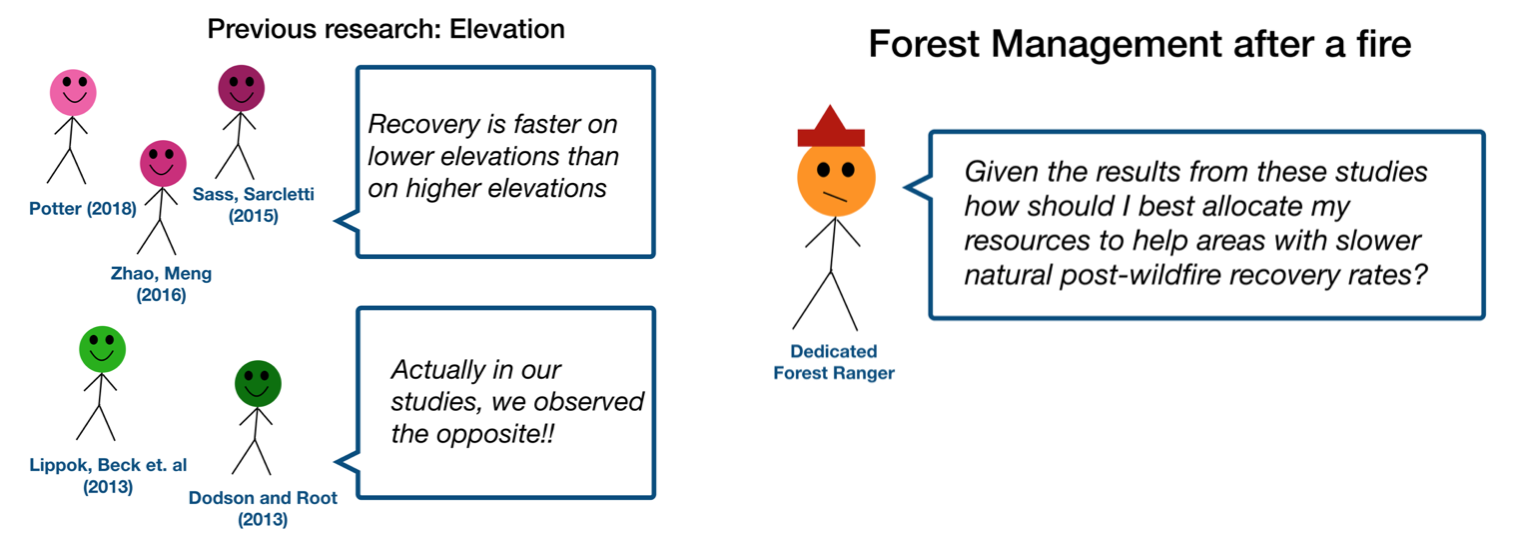
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

- Personal Finance
- Practice Management
- Early Career and Young Professionals
- The Specialist Series
- Business Management Resources
- Personal Finances Resources
- Podcasting Resources
- SoMeDocs: Doctors on Social Media
- Online Courses
- Recommended Books
- Recommended Blogs, Websites, and Podcasts
- Work with Me
- The Scope of Practice Podcast
- All Episodes
- The Sunday Special
- Women in Medicine
- Apply to be a guest on The Scope of Practice Podcast
- Recommended Podcasts
- Invite Brent to be a guest on your podcast
Written by Brent Lacey on July 5, 2020 . Posted in Early Career and Young Professionals , Practice Management .
17 “Do’s” and “Don’ts” for Giving a Great Presentation

Public speaking is the #1 fear for a huge percentage of people . It’s above the fear of dying for many people. How can you think about giving a great presentation when you’re worried about even giving a basic presentation?
I’ve been doing public speaking events for over a decade, but it definitely wasn’t an easy journey. It’s hard to get comfortable talking in front of groups of 10 people, let alone a hundred or a thousand. Still, this is a skill that you can learn and even master with some study and practice.
Let’s look at some major “do’s” and “don’ts” for creating a great presentation.

11 “Do’s” for Giving a Great Presentation
1. believe that giving a great presentation is a learnable skill..
Giving a good presentation is a learnable skill. Even true introverts can give excellent presentations. In fact, introverted people actually tend to plan better presentations though they may be more afraid to give them. Extroverts are more likely to “wing it” but are more naturally comfortable being on a stage.
Both approaches have value, but both have their pitfalls. Learning to give a great speech isn’t like putting a hammer to a nail. It’s an organic process, and it takes time to get good at it. But, through practice and repetition, you can be an amazing presenter !
2. Prepare for the presentation!
It takes a tremendous amount of work to make something appear effortless. My general rule of thumb is to allocate 45-60 minutes of preparation time for every 5 minutes of speaking time . So, for an hour-long presentation, I may prepare 10-12 hours ahead of time.
One important question is whether script the entire speech. It depends on what you’re speaking about, but it’s generally advisable to not script 100% of your remarks. It’s good to rehearse but not “sound rehearsed.” Outline the presentation, make notes of any stories you want to tell and major points to drive home. But, it’s not critical that you script every single word.
You can also prepare by having great-looking slides that will impress your audience. That will give you more confidence going into the presentation.
3. When you’re with your peers, it’s ok to “speak your geek.”
Know your audience! If you’re speaking to a group of colleagues, you don’t need to “dumb things down.” It’s good to speak in layman’s terms with patients and audiences who are unfamiliar with your work. However, with peers, feel free to use technical jargon that’s widely understood.
4. Use stories to transform your communication.
Listeners will only remember data 5% of the time, but they’ll remember stories 60% of the time . That’s because stories are how we naturally communuicate ! Our brains are wired to think that way.
Listen to the podcast episode with Nancy Duarte to learn the formula for creating the most memorable story.
Every presentation is more memorable with stories. In fact, stories may be the only parts of your presentation that anyone remembers. One thing you can do is build a “story library” for yourself. Basically, that’s a collection of 10-20 stories that are memorable/impactful to you that you can pull out and use in a variety of different presentations when the need arises.
5. Develop a good “pre-talk ritual.”
Immediately prior to your presentation, what are you doing to get yourself ready to go up on stage? Some people like to “pump themselves up,” and others prefer to “calm themselves down.” I’m more of a calm-yourself-down kind of presenter.
If I’m presenting at a conference, for example, I like to sit in on the presentation right before mine and just listen. I shut my brain off and don’t think about my presentation at all. It’s helpful for me to be calm and just relax. Otherwise, I find that I “get in my head” too much and I start getting anxious.
I know other people that prefer to listen to some Rocky music and box an imaginary punching bag. Whatever your needs, pick a pre-talk ritual that helps you get in the right frame of mind so you can go out on that stage and crush it!
6. Follow the structure of a great presentation as outlined in Nancy Duarte’s podcast episode.
Jump to 19:52 to hear Nancy eloquently express the formula of a great presentation. This is backed by thousands of analyses from the greatest speeches in history.
7. Use repetition, familiar phrases, imagery, and metaphors to help transport the audience.
If you’ve ever listened to Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech, you’ll hear him use a lot of references that would have been familiar to his audience. These references include Scriptures, hymns, and cultural references.
He also used repetition to great effect. The phrase “I have a dream” appears 8 times in his speech. That repetition made the speech more memorable and helped transport the audience to a new plane of comprehension.
8. Have the right level of emotional appeal to fit your audience.
Passion and emotion are good, but it needs to fit the “mood” of the audience to some degree. You’re probably not going to do well giving a eulogy if you’re yelling and pumping people up like it’s halftime at the Super Bowl.
Emotional appeals are good and can help audience members feel the weight of your words in a more high-impact way. Just make sure to “read the room” as you consider how to bring emotion into the presentation. Sitting in the presentation before yours can be a great way to gauge how the people in the room are feeling.
9. Use your presentation to translate to real growth in your business.

If you’re doing public speaking, what’s the point? That is, what value does the speaking engagement bring to your business? If you’re just in it to make money or get some experience, that’s fine as far as that goes. But, a speaking engagement could be more valuable in propelling your business growth forward.
Are you going to a conference ? You can network with other presenters and look for opportunities to collaborate. You could meet the attendees and perhaps earn some new clients.
Speeches can also help establish you as a thought leader. If your speech is being recorded, a great presentation can even be an opportunity for free promotion.
Whatever your plan, be intentional! If you get invited to speak at an event, take that opportunity and use it for real business growth!
10. Use a speaking coach.
I haven’t used a speaking coach before, but I’ve definitely been considering it since my interview with Nancy Duarte . Even the most seasoned veterans can benefit from coaching.
A good speaking coach can show you how to change your inflection, insert pauses and places to emphasize your points, and help you craft the structure of your speech. You might not be able to afford one when you’re first starting out, but it’s worth considering if you’re going to be doing public speaking on a regular basis.
11. Use data to support your presentation.
Data are important to support the validity and authority of your talk, but you’ve got to weave it effectively into the story structure. Don’t just spout random bits of data with no context. Offer the data as supporting evidence within your story narrative.
6 “Don’ts” for Giving a Great Presentation
1. don’t be the hero in your story..
Always be the guide in your story ! The audience is the hero. You don’t want to be Luke Skywalker! You want to be Yoda!! The hero is the lead character in the story. If you make yourself the hero, the audience who already thinks of themselves as the hero sees you as competition in the story.
If you play the guide instead, the audience looks to you to help them solve their problems. Always be the guide, not the hero!!
2. Don’t be afraid to speak “off the cuff” occasionally.
I don’t generally advise “winging it,” but sometimes a little extemporaneous speaking is called for. This is where the “story library” idea can come in handy. You may be able to tell the same story in a variety of settings and emphasize different aspects of the story each time. This strategy can give the feel of spontaneity but with the confidence of you generally knowing what you’re going to say.

3. Don’t create slides in a “linear fashion.”
When you’re creating a slide deck, don’t just do it in a linear fashion (e.g. slide 1, slide 2, etc). Start with the “guiding light” or main central point, and then every slide serves to drive home that central point. You should be constantly driving your audience towards that central point. All slides support that central point because it may be the only point your audience remembers.
4. Don’t read directly off the powerpoint slides.
I have gotten up and left in the middle of lectures when the lecturer was reading directly off the slides. It’s so boring! I can read faster than they talk. They aren’t saying anything new by the time I’m finished reading, so I’m ready to move on to the next thing.
Powerpoint slides are fine, and you can even use it as a sort of teleprompter, but just don’t read directly off it! Did you know you can hit the “B” button to turn your screen black or “W” to turn the screen white? Then, you could use the powerpoint as a teleprompter and the audience doesn’t see it.
Put one central point on each slide and use it as a way to jog your memory for what you want to say. You can have a couple of hundred slides with only one point or image per slide and it’s better than having 20 that are jam-packed with too much info.
5. Don’t use the podium as a crutch.
Move around the stage! It projects confidence and keeps the audience engaged. The best way to feel comfortable moving around the stage is spending a lot of time preparing the presentation beforehand. Then, you’ll feel more confident breaking away from the podium.
6. Don’t be so afraid of public speaking that you never give it a try!
Public speaking is a genuine fear for a lot of people, but it’s so much fun! You can do it! Just give it a shot!
Final Thoughts
Public speaking isn’t an innate talent, and it’s not limited to extreme extroverts and “naturally charismatic” people. Anyone can learn to be a public speaker. If you’re worried about how it’ll go, start small. Join the Toastmasters or similar club in your area. Get with a speaking coach. Read, study, and learn the tips and techniques of the best speakers.
Then, start looking for opportunities to speak to others. Start with yourself, your friends, and your family. Move up to local clubs and organizations, then gradually step it up from there. There’s so much value in being good at public speaking, and I think it’s worth it to step out in faith and try!
Further Reading
- Listen to the companion podcast episode with Nancy Duarte
- 5 Big Mistakes Physicians Make with Social Media
- What Makes a Great Physician Leader? 10 Lessons from a Surgeon General.
Please leave a comment below! What’s your top tip for someone interested in public speaking?
Full Disclosure: Some of the links to the resources listed above may be affiliate links, which means that I will receive a small commission if you click through and make a purchase. But it doesn’t cost you anything extra—it’s just a way to show you appreciate what we do here. Thanks for this.
Related posts:
business , dentist , leadership , marketing , personal growth , physician , practice management
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment

- Early Career & Young Professionals
- All Articles
- Additional Resources
- Specialist Series
- Subscribe to Network
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 The Scope of Practice. All Rights Reserved.


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Top Tips for Effective Presentations
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
How can you make a good presentation even more effective?
This page draws on published advice from expert presenters around the world, which will help to take your presentations from merely ‘good’ to ‘great’.
By bringing together advice from a wide range of people, the aim is to cover a whole range of areas.
Whether you are an experienced presenter, or just starting out, there should be ideas here to help you to improve.
1. Show your Passion and Connect with your Audience
It’s hard to be relaxed and be yourself when you’re nervous.
But time and again, the great presenters say that the most important thing is to connect with your audience, and the best way to do that is to let your passion for the subject shine through.
Be honest with the audience about what is important to you and why it matters.
Be enthusiastic and honest, and the audience will respond.
2. Focus on your Audience’s Needs
Your presentation needs to be built around what your audience is going to get out of the presentation.
As you prepare the presentation, you always need to bear in mind what the audience needs and wants to know, not what you can tell them.
While you’re giving the presentation, you also need to remain focused on your audience’s response, and react to that.
You need to make it easy for your audience to understand and respond.
3. Keep it Simple: Concentrate on your Core Message
When planning your presentation, you should always keep in mind the question:
What is the key message (or three key points) for my audience to take away?
You should be able to communicate that key message very briefly.
Some experts recommend a 30-second ‘elevator summary’, others that you can write it on the back of a business card, or say it in no more than 15 words.
Whichever rule you choose, the important thing is to keep your core message focused and brief.
And if what you are planning to say doesn’t contribute to that core message, don’t say it.
4. Smile and Make Eye Contact with your Audience
This sounds very easy, but a surprisingly large number of presenters fail to do it.
If you smile and make eye contact, you are building rapport , which helps the audience to connect with you and your subject. It also helps you to feel less nervous, because you are talking to individuals, not to a great mass of unknown people.
To help you with this, make sure that you don’t turn down all the lights so that only the slide screen is visible. Your audience needs to see you as well as your slides.
5. Start Strongly
The beginning of your presentation is crucial. You need to grab your audience’s attention and hold it.
They will give you a few minutes’ grace in which to entertain them, before they start to switch off if you’re dull. So don’t waste that on explaining who you are. Start by entertaining them.
Try a story (see tip 7 below), or an attention-grabbing (but useful) image on a slide.
6. Remember the 10-20-30 Rule for Slideshows
This is a tip from Guy Kawasaki of Apple. He suggests that slideshows should:
- Contain no more than 10 slides;
- Last no more than 20 minutes; and
- Use a font size of no less than 30 point.
This last is particularly important as it stops you trying to put too much information on any one slide. This whole approach avoids the dreaded ‘Death by PowerPoint’.
As a general rule, slides should be the sideshow to you, the presenter. A good set of slides should be no use without the presenter, and they should definitely contain less, rather than more, information, expressed simply.
If you need to provide more information, create a bespoke handout and give it out after your presentation.
7. Tell Stories
Human beings are programmed to respond to stories.
Stories help us to pay attention, and also to remember things. If you can use stories in your presentation, your audience is more likely to engage and to remember your points afterwards. It is a good idea to start with a story, but there is a wider point too: you need your presentation to act like a story.
Think about what story you are trying to tell your audience, and create your presentation to tell it.
Finding The Story Behind Your Presentation
To effectively tell a story, focus on using at least one of the two most basic storytelling mechanics in your presentation:
Focusing On Characters – People have stories; things, data, and objects do not. So ask yourself “who” is directly involved in your topic that you can use as the focal point of your story.
For example, instead of talking about cars (your company’s products), you could focus on specific characters like:
- The drivers the car is intended for – people looking for speed and adventure
- The engineers who went out of their way to design the most cost-effective car imaginable
A Changing Dynamic – A story needs something to change along the way. So ask yourself “What is not as it should be?” and answer with what you are going to do about it (or what you did about it).
For example…
- Did hazardous road conditions inspire you to build a rugged, all-terrain jeep that any family could afford?
- Did a complicated and confusing food labelling system lead you to establish a colour-coded nutritional index so that anybody could easily understand it?
To see 15 more actionable storytelling tips, see Nuts & Bolts Speed Training’s post on Storytelling Tips .
8. Use your Voice Effectively
The spoken word is actually a pretty inefficient means of communication, because it uses only one of your audience’s five senses. That’s why presenters tend to use visual aids, too. But you can help to make the spoken word better by using your voice effectively.
Varying the speed at which you talk, and emphasising changes in pitch and tone all help to make your voice more interesting and hold your audience’s attention.
For more about this, see our page on Effective Speaking .
9. Use your Body Too
It has been estimated that more than three quarters of communication is non-verbal.
That means that as well as your tone of voice, your body language is crucial to getting your message across. Make sure that you are giving the right messages: body language to avoid includes crossed arms, hands held behind your back or in your pockets, and pacing the stage.
Make your gestures open and confident, and move naturally around the stage, and among the audience too, if possible.
10. Relax, Breathe and Enjoy
If you find presenting difficult, it can be hard to be calm and relaxed about doing it.
One option is to start by concentrating on your breathing. Slow it down, and make sure that you’re breathing fully. Make sure that you continue to pause for breath occasionally during your presentation too.
For more ideas, see our page on Coping with Presentation Nerves .
If you can bring yourself to relax, you will almost certainly present better. If you can actually start to enjoy yourself, your audience will respond to that, and engage better. Your presentations will improve exponentially, and so will your confidence. It’s well worth a try.
Improve your Presentation Skills
Follow our guide to boost your presentation skills learning about preparation, delivery, questions and all other aspects of giving effective presentations.
Start with: What is a Presentation?
Continue to: How to Give a Speech Self Presentation
See also: Five Ways You Can Do Visual Marketing on a Budget Can Presentation Science Improve Your Presentation? Typography – It’s All About the Message in Your Slides
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Introduce Yourself Before Giving a Seminar
Last Updated: December 23, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 417,654 times.
Giving a seminar is an exciting opportunity to share your professional or academic knowledge. No matter who your audience is, begin your presentation with a personal introduction to give the attendees some context about why you’re there. We know how much work goes into preparing for public speaking, so we’ve put together this list of tips to help make introducing yourself a breeze!
Stand up straight.

- This can also help if you’re feeling a little nervous before giving your seminar. A powerful stance helps you feel more confident in yourself as well.
Smile at the attendees.

- Smiling is another thing that can help you feel confident about your presentation before you get into it. This is because it releases endorphins that can calm down anxious feelings.
- Your presentation instantly comes from a very strong place when you start with a big smile, lots of energy, and lots of volume.
Chat with people before the seminar starts.

- For example, if you’re giving a seminar about psychology at a university and you’re up at the front of the classroom with some audience members who are already seated in the front row, you can say something like: “Hi everyone, thanks for coming. Are you all psychology majors?”
Keep your introduction short.

- This is your chance to get the audience’s attention. If you go on too long about yourself before you even get into the content of your seminar, the people might just tune you out right from the start.
Start with your name.

- For example, say something like: “Hi everybody, thank you all so much for coming today. My name is Bob Johnson.”
- If you have any professional titles, such as “Doctor,” include those when you say your name as well.
State your company or profession.

- For instance, say something like: “I’m with Creative Consulting LLC.” Or, say something like: “I work in the marine biology department.”
Say what your specialty is.

- For example, say something along the lines of: “Our specialty is working with new companies to develop their brand’s identity.” Another idea is something like: “My specialty is studying local marine life along Washington’s coast.”
Give an overview of your background.

- For example, you can say: “I studied public relations and journalism at Washington State University and I’ve worked in marketing for almost 10 years now.” Or, say: “I’ve taught marine biology 101 and 209 here on campus for the past 8 years, as well as being involved in the research program for the past 5 years.”
Provide more personal info that you feel is important.

- For instance, you could say: “I’m originally from Canada, but I’ve lived in Washington for half my life now.” Or, say: “When I’m not helping companies with their marketing strategies, I like to go skydiving.”
Introduce your seminar topic.

- For example, say: “In the past decade, we’ve seen a drastic reduction in the native whale populations along Washington’s coast. Today I’m going to compare the current whale activity with that of the 90s, discuss why the population has declined so much, and propose some ways to help the population bounce back over the coming decade.”
- It can be good to introduce your seminar topic intro with an attention-grabbing fact. For instance, if your presentation is about homelessness in Seattle, say: “Every night, more than 3,000 people sleep on the streets of Seattle.”
- It's also helpful to take the audience on a little journey into their won experience. You might start off with a statement like "Think back on your happiest childhood memory..." or "What was the scariest moment of your life?"
Practice your intro ahead of time.

- Your whole intro might go a bit like this: “Hi everyone, thanks so much for coming today. My name is Sarah Ramirez and I’m with Red Door Recruiting. My specialty is recruiting for the finance industry. I studied business at USC and I’ve worked in recruitment for 5 years now. Every year, 25,000 students graduate from our state’s universities and start seeking employment. Today, I want to discuss some of the new platforms and technologies we have for finding and connecting with those new professionals.”
Expert Q&A

Tips from our Readers
- Make eye contact with the audience by looking slightly above people’s heads.
- Be confident in what you have to say!
You Might Also Like

Expert Interview
Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about introducing yourself, check out our in-depth interview with Patrick Muñoz .
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/intl/blog/prefrontal-nudity/201209/standing-confidence
- ↑ https://positivepsychology.com/self-confidence/
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2017/02/tips-speaking
- ↑ https://hbr.org/2019/09/to-overcome-your-fear-of-public-speaking-stop-thinking-about-yourself
- ↑ https://hbr.org/2022/08/a-simple-way-to-introduce-yourself
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/members/content/public-speaking
- ↑ https://www.engineering.iastate.edu/ecs/students/the-employment-process/the-employment-process-for-graduate-students/interviewing-as-a-graduate-student/on-site-interviewing/interview-seminar/
- ↑ https://www.luc.edu/media/lucedu/lurop/pdfs/Guide%20to%20Oral%20Presentation%20Introductions.pdf
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/ed/precollege/psn/2019/02/skillful-student
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Purity Obiora
Aug 7, 2017
Did this article help you?
Oct 8, 2016
Salman Akhtar
Nov 15, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

200 Seminar Topics

As a dynamic seminar leader, it’s crucial to have a roster of stimulating and thought-provoking topics. These 200 seminar topics are designed to ignite lively discussions and enrich your upcoming sessions!
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence: Opportunities and Challenges
- Climate Change and Sustainability Practices
- The Impact of Social Media on Society
- Cybersecurity in the Digital Age
- The Ethics of Genetic Engineering
- Mental Health Awareness in the Workplace
- The Role of Blockchain in Financial Services
- The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles
- Space Exploration and Colonization
- The Power of Mindfulness and Meditation
- The Digital Divide: Bridging the Gap
- Renewable Energy: Prospects and Technologies
- Big Data Analytics and Its Applications
- The Importance of Vaccination: Myths vs. Facts
- The Gig Economy and the Future of Work
- Globalization and Its Effects on Cultures
- The Psychology Behind Consumer Behavior
- Women Empowerment and Gender Equality
- The Evolution of Smart Cities
- The Significance of Biodiversity Conservation
- Nanotechnology: The Next Big Thing?
- The Effects of Overpopulation
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Beyond the Buzzword
- The Influence of Celebrity Endorsements on Consumer Choice
- Waste Management Solutions for Urban Areas
- The Realities of Virtual Reality
- The Economics of Happiness
- The Science of Sleep and Its Importance
- Artificial Organ Transplantation: Progress and Ethics
- The Effectiveness of Online Education
- Mitigating the Risks of Nuclear Energy
- Augmented Reality in Modern Marketing
- The War on Plastic: Alternatives and Innovations
- Understanding the Human Microbiome
- Civil Liberties in the Digital Era
- Overcoming Language Barriers Through Technology
- The Advent of Quantum Computing
- The Implications of Sea-Level Rise
- Protecting Identity in the Age of Information
- Modern Piracy on the High Seas
- The Intersection of Art and Technology
- The Revival of Traditional Medicine
- The Dynamic World of Entrepreneurship
- Encouraging Innovation in Education
- Food Security: A Global Perspective
- The Age of Information Overload
- Advancements in Water Purification Technology
- Universal Basic Income: Feasibility and Function
- The Decline of Reading in the Digital Age
- The Challenge of Maintaining Privacy Online
- The Human Impact on Coral Reefs
- The Future of Drones in Civilian Life
- A World Without Borders: Prospects and Pitfalls
- Stem Cell Research: Promise and Controversy
- The Progress of Telemedicine
- Social Entrepreneurship for Sustainable Development
- The Fight Against Antimicrobial Resistance
- Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
- Media Literacy in the Age of Fake News
- The Economics of Climate Change
- The Psychology of Social Networks
- Exploring the Deep Ocean: Mysteries and Discoveries
- Free Speech in the Age of the Internet
- The Emergence of E-Sports
- The Role of NGOs in Global Governance
- Automation and Job Displacement
- The Impacts of Urban Green Spaces
- The Reality of Living in a Post-Truth World
- The Impact of Tourism on Local Communities
- The Future of Biometrics in Security
- Mitigating Natural Disasters through Technology
- Quantum Cryptography and Data Security
- Dissociative Identity Disorder: Myths and Facts
- The Role of Science Fiction in Shaping the Future
- Deforestation: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
- Explaining the Gigapixel Imaging Revolution
- Urban Farming and the Local Food Movement
- The Evolution of International Trade Agreements
- The Power of Placebo in Modern Medicine
- The Consequences of Economic Sanctions
- The Renaissance of Podcasting
- Understanding Eating Disorders
- Telecommuting: Redefining Work-Life Balance
- The Rise of Dark Tourism
- Addressing the Opioid Crisis
- The Psychology of Video Games
- The Internet of Things and Smart Homes
- The Rising Popularity of Minimalism
- The Changing Landscape of Journalism
- Developing Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
- The Global Water Crisis
- The Future of 3D Printing in Manufacturing
- The Benefits and Risks of GMOs
- The Impact of Driverless Cars on Society
- Confronting the Obesity Epidemic
- The Importance of Digital Literacy
- Exploring the Multiverse Theory
- The Psychology of Persuasion and Influence
- The Growth of Renewable Energy in Developing Countries
- The Threat of Superbugs and Antibiotic Resistance
- The New Age of Space Tourism
- The Social Impact of eSports
- The Revolution in Electric Mobility
- The Healing Power of Music Therapy
- The Risks and Rewards of Crowdfunding
- The Cultural Implications of Memes
- Facial Recognition Technology: Security vs. Privacy
- The Shift Towards Cashless Economies
- The Growing Issue of Tech Addiction
- Exploring the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- The Intersection of Genetics and Athletics
- The Rise of Citizen Journalism
- Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
- The Debate Over Net Neutrality
- The Psychology of Procrastination
- Vertical Farming: The Future of Agriculture?
- The Threats to Net Neutrality
- The Growth of Virtual Reality Gaming
- Wearable Technology and Health Monitoring
- The Promise of Personalized Medicine
- Tackling the Fast Fashion Industry
- The Rise of Influencer Marketing
- The Impact of Language on Thought
- The Complex World of Cryptocurrency
- The Use of Drones in Agriculture
- Understanding Postpartum Depression
- The Challenges of Cross-Cultural Communication
- The Ethical Dilemmas of Driverless Cars
- The Global Impact of Human Trafficking
- The Benefits of Forest Bathing
- Addressing Homelessness: Policy and Social Work
- The Importance of Bees in Our Ecosystem
- The Psychological Effects of Social Isolation
- The Role of Art in Emotional Healing
- The Power of Positive Thinking
- The Role of Youth in Politics
- The Revival of Indigenous Languages and Cultures
- The Future of Classroom Technology
- The Environmental Costs of Fast Fashion
- The Societal Effects of Reality Television
- Achieving Work-Life Harmony in Modern Society
- The Importance of Critical Thinking in Education
- The Challenges of Wildlife Conservation
- The Quest for Artificial Superintelligence
- The Surprising Science of Happiness
- The Potential of Hydrogen as a Clean Energy Source
- The Growing Popularity of Telehealth
- The Future of Retail in the Digital Age
- Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders
- The Socioeconomic Impact of Sports
- The Role of Meditation in Stress Reduction
- The Power of Play in Child Development
- The Ethics of Surveillance in Society
- The Future of Nanomedicine
- The Importance of Financial Literacy
- The Potential of Seasteading Communities
- The Therapy of Animal Assisted Interventions
- The Changing Dynamics of Modern Families
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Education
- The Effect of Music on Cognitive Performance
- The Challenges of Urban Transportation Planning
- The Threat of Deepfake Videos
- Cultivating Leadership Skills in Youth
- The Political Psychology of Elections
- The Impact of Language Learning on Cognitive Abilities
- The Role of Public Art in Urban Spaces
- The History and Future of Nuclear Energy
- Plant-Based Diets and Sustainability
- The Role of International Law in Global Conflict Resolution
- The Resurgence of Populism in Global Politics
- The Future of Gene Editing: CRISPR and Beyond
- The Challenges of Overfishing and Ocean Conservation
- The Legal and Ethical Implications of AI Decision-Making
- The Growing Market of Smart Wearables
- The Health Benefits of Urban Gardening
- The Age of Instant Gratification and Its Consequences
- The Dynamics of International Space Law
- The Science Behind Effective Learning Strategies
- The Growing Field of Eco-Tourism
- The Rise of Digital Literature and E-Readers
- The Legacy of Colonialism in Modern Politics
- The Relationship Between Diet and Mental Health
- The Future Landscape of Biotech Farming
- The Relevance of Philosophy in Contemporary Society
- The Social Consequences of Income Inequality
- Cultivating Creativity in Education
- The New Frontier of Brain-Computer Interfaces
- The Role of Animals in Therapy and Rehabilitation
- The Continuing Challenge of Nuclear Non-Proliferation
- The Power of Storytelling in Marketing
- The Role of Public Health Policies in Shaping Societies
- The Psychological Impact of Natural Disasters
- The Ethical Implications of Cloning Technologies
- The Influence of Digital Nomadism on Work Culture
- Deep Learning and the Future of Artificial Intelligence
- The Battle Against Cyberbullying
- The Rise of Subscription-Based Business Models
- The Intersection of Ethics and Professional Sports
- The Growing Threat of Cyber Warfare
- The Psychological Effects of Urbanization
Related Posts:

- Products and Courses
- Marketing And Sales Automation
- Membership and Coaching
- Case Studies
- Client Reviews
- Meet Our Team
- Meet Our Consultants
- MSP Marketing Guide
- MSP SEO Guide
- MSP Social Media Guide
- How To Sell Managed Services
- Call: 615-790-5011

How To Give A Seminar Presentation That Sells Your IT Services
Robin Robins August 8, 2017 IT Managed Services , IT Marketing , IT Sales

Why Seminars Are Powerful Tools For Promoting Your IT Services
You’re positioned as an expert, you earn trust faster than cold calling, you have your target audience’s full attention, how to overcome the fear of public speaking, speak in small groups, over-prepare, how to give a seminar presentation that sells.
- What is the outcome or result you want from delivering this presentation?
- How will you measure the success of your presentation?
Ask For the Sale In The Presentation
Highlight the value of what you’re selling.
- Establish WHY a business needs regular network maintenance and monitoring
- Provide case studies and testimonials of other businesses you have helped that demonstrate tangible business results
- Establish credibility for your company
- Clearly demonstrate why your IT services are superior to other managed services plans
- Recognize and overcome common sales objections
- Clearly define the measurable and tangible results this system will deliver, and guarantee them
- Close your presentation with an offer for a free network audit or another valuable service that only attendees who act that day can access
Close Strong
Avoid the “consultative” seminar presentation, is the fear of selling hurting your seminar presentation.
- “That’s just not me.”
- “That’s just not the way we do things.”
- “We haven’t had to use this in the past and won’t start now.”
Related Posts

An Easy To Implement Marketing Strategy That Will Help You Close Large IT Managed Services Sales, Faster And Easier By: Robin Robins, Author…
Have you seen the latest product called P.B. Slices? It’s peanut butter formed into pre-packaged slices like cheese so you don’t have to spread it…
- Products And Courses
- Membership And Coaching
- Member Login
- Call 615-790-5011
- MSP Marketing Strategies

- People Directory
- Safety at UD

- Campus & Community
- Nation & World
- Culture & Society

CISO candidate presentation on Aug. 13
Article by IT Communication Group August 06, 2024
UDIT’s candidate to give a presentation on the future of cybersecurity strategy in higher ed
One of the candidates for chief information security officer (CISO) at the University of Delaware will be delivering a presentation on the future of higher education cybersecurity strategy on Tuesday, Aug. 13.
Event Details: Date: Aug. 13, 2024 Time: 2-3 p.m. (includes time for Q&A) Location: Mitchell Hall—134 The Green
This presentation will provide valuable insights into the evolving landscape of cybersecurity in higher education. It's a great opportunity to learn more about the candidate's vision and expertise in this critical area.
The event can be attended in person or via live stream. The livestream link can be accessed at sites.udel.edu/udlive . CAS login is required.
More Inside UD Stories
Portuguese students visit ud to learn about u.s. financial system.
August 06, 2024
Article by Jen Hendrickson
CISO candidate presentation on Aug. 6
August 02, 2024
Article by IT Communication Group
UD faculty invited to lead Delaware Teachers Institute seminar
August 01, 2024
Article by Jon Cox
See More Stories
Subscribe to UDaily >
Have a udaily story idea.
Contact us at [email protected]
Members of the press
Contact us at 302-831-NEWS or visit the Media Relations website
ADVERTISEMENT
- Campus & Community
- Nation & World
- Culture & Society
- UD Magazine
- In Memoriam
- Media Experts
Office of Communications & Marketing 105 E. Main St. Newark, DE 19716 [email protected] Phone: 302-831-2792
- How to Login
- Use Teams on the web
- Join a meeting in Teams
- Join without a Teams account
- Join on a second device
- Join as a view-only attendee
- Join a breakout room
- Join from Google
- Schedule a meeting in Teams
- Schedule from Outlook
- Schedule from Google
- Instant meeting
- Add a dial-in number
- See all your meetings
- Invite people
- Meeting roles
- Add co-organizers
- Hide attendee names
- Tips for large Teams meeting
- Lock a meeting
- End a meeting
- Manage your calendar
- Meeting controls
- Prepare in a green room
- Present content
- Share slides
Share sound
- Apply video filters
- Mute and unmute
- Spotlight a video
- Multitasking
- Raise your hand
- Live reactions
- Take meeting notes
- Customize your view
- Laser pointer
- Cast from a desktop
- Use a green screen
- Join as an avatar
- Customize your avatar
- Use emotes, gestures, and more
- Get started with immersive spaces
- Use in-meeting controls
- Spatial audio
- Overview of Microsoft Teams Premium
- Intelligent productivity
- Advanced meeting protection
- Engaging event experiences
- Change your background
- Meeting themes
- Audio settings
- Manage attendee audio and video
- Reduce background noise
- Voice isolation in Teams
- Mute notifications
- Use breakout rooms
- Live transcription
- Language interpretation
- Live captions
- End-to-end encryption
- Presenter modes
- Call and meeting quality
- Meeting attendance reports
- Using the lobby
- Meeting options
- Record a meeting
- Meeting recap
- Play and share a meeting recording
- Delete a recording
- Edit or delete a transcript
- Customize access to recordings or transcripts
- Switch to town halls
- Get started
- Schedule a live event
- Invite attendees
- organizer checklist
- For tier 1 events
- Produce a live event
- Produce a live event with Teams Encoder
- Best practices
- Moderate a Q&A
- Allow anonymous presenters
- Attendee engagement report
- Recording and reports
- Attend a live event in Teams
- Participate in a Q&A
- Use live captions
- Schedule a webinar
- Customize a webinar
- Publicize a webinar
- Manage webinar registration
- Manage what attendees see
- Change webinar details
- Manage webinar emails
- Cancel a webinar
- Manage webinar recordings
- Webinar attendance report
- Get started with town hall
- Attend a town hall
- Schedule a town hall
- Customize a town hall
- Host a town hall
- Use RTMP-In
- Town hall insights
- Manage town hall recordings
- Cancel a town hall
- Can't join a meeting
- Camera isn't working
- Microphone isn't working
- My speaker isn’t working
- Breakout rooms issues
- Immersive spaces issues
- Meetings keep dropping

Present content in Microsoft Teams meetings
When working remotely in Microsoft Teams, you can present content by sharing your screen, your entire desktop, a PowerPoint file, and more.
Start presenting content

Note: If you're using Teams on the web, you'll be able to share your screen only if you're using Google Chrome or the latest version of Microsoft Edge. Screen sharing isn't available for Linux users.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | Show your entire screen, including notifications and other desktop activity. | You need to seamlessly share multiple windows. |
| Window | Show just one window, and no notifications or other desktop activity. | You only need to show one thing and want to keep the rest of your screen to yourself. |
| PowerPoint Live | Present a PowerPoint file others can interact with. | You need to share a presentation and want others to be able to move through it at their own pace. For info on PowerPoint sharing, see . |
| Whiteboard | Collaborate with others in real time. | You want to sketch with others and have your notes attached to the meeting. |
When you're done sharing, select Stop sharing in your meeting controls.
To turn off screensharing if your screen locks:

Turn the Turn off my camera and mic when my screen locks toggle on.
Restart Teams to activate this setting.
Presenter controls
While you're sharing content, use the controls in the presenter toolbar to keep your presentation engaging and running smoothly. The presenter toolbar is only visible to the person presenting.
To bring the presenter toolbar onscreen:
The toolbar will stay in place for a few seconds until you're done adjusting the controls. Then, it'll disappear from view.
Move the presenter toolbar
To keep the presenter toolbar from blocking important content on your screen, move it to any area on the screen you're sharing.
To move the presenter toolbar:

Drag it anywhere on your screen.
Release the drag handle when you've placed it in the right area.
Tip: You can also move the toolbar by clicking and holding any area on the toolbar that isn't interactive (e.g., in between presenter controls) and dragging it.
Control your camera and mic

Give and take control of shared content
Give control.
If you want another meeting participant to change a file, help you present, or demonstrate something, you can give control to that person. While someone has control, they can make selections, edits, and other modifications to the shared screen.
You'll both be in control of the sharing, and you can take back control anytime.
Caution: When you’re sharing an app, only give control to people you trust . People you give control can send commands that could affect your system or other apps. We've taken steps to prevent this but haven't tested every possible system customization.
Start sharing your screen.

Select the person you want to give control to. Teams will notify them that you’re sharing control.
Select Take back to take back control.
Take control
To take control while another person is sharing:
Select Request control . The person sharing can approve or deny your request.
Make selections, edits, and other modifications to the shared screen while you have control.
Select Release control to stop sharing control.
Sharing computer sound lets you stream audio from your computer to meeting participants through Teams. You can use it to play a video or audio clip as part of a presentation.
To learn more, see Share sound from your computer in a Teams meeting or live event .
All sound from your computer, including notifications, will be audible in the meeting.
Optimize for video
Prevent choppiness or lag when you're sharing high-motion content by optimizing video.
To optimize video, select Optimize in your presenter toolbar.

Change your layout
When you're sharing content, you can choose from several different layouts to help make your presentation more engaging.
To change your layout while you're sharing your screen:
Turn your camera on.

Select the layout you want to use:
Content only : Participants will see the content you're sharing in the main Teams window. They'll still be able to see your video feed next to the content.
Standout : This produces an effect on your background that blocks it and helps you stand out in your video feed.
Side-by-side : This view will place you and another participant side-by-side in the meeting window. This helps draw focus to you and other participants who are speaking during the meeting.
Reporter : This layout isolates you from your video feed and places you in front of the content you're sharing, just like a reporter in front of a scene.
Annotate content
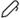
To learn more, see Use annotation while sharing your screen in Microsoft Teams .
View participants
After you start presenting, a minimized view of the meeting window will appear next to your shared content.

Stop sharing
Select Stop sharing in the presenter toolbar to stop sharing your screen and return to the main Teams meeting window.
Share content on a Mac
If you're using a Mac, you'll need to grant permission to Teams to record your computer's screen before you can share.
You'll be prompted to grant permission the first time you try to share your screen. Select Open System Preferences from the prompt. If you miss the prompt, you can do this anytime by going to Apple Menu > System Settings > Privacy & Security .
Under Screen & System Audio Recording , make sure the toggle next to Microsoft Teams is turned on.
Go back to your meeting and try sharing your screen again.
Note: If you're using Teams on the web, make sure you've also granted screen recording permission to your browser.
Zoom in to shared content
To get a better look at shared content, click and drag it to see different areas. To zoom into or out of content someone's sharing during a meeting or call, use the buttons at the lower left of your meeting window: [+] to zoom in and [-] to zoom out. You can also try the following:
Pinch in or out on your trackpad.
Use Teams keyboard shortcuts .
Hold the Ctrl key and scroll with your mouse.
Note: Mac trackpads don't support zoom in meetings. If you're on a Mac, use one of the other options. If you're using Linux, giving and taking control of shared content isn't available at this time.
Open shared content in new window
Expand your view by opening shared content in a separate window during your Teams meetings.
To open shared content:
Join your meeting from Teams for desktop .

To minimize content, select X to close the window.
Share content
To share content from your mobile device:

| Choose... | If you want to... |
|---|---|
|
| Present a PowerPoint file others can interact with. Choose the PowerPoint you want to share; when you select one, sharing will start automatically. |
|
| Take a photo to share or choose one from your gallery. Choose the photo you want to share and select when you're ready to share. |
|
| Share live video from your camera. Tap when you're ready to share. |
|
| Show your entire screen, including notifications and other activity. You'll be prompted to tap when you're ready to share. Turn on the toggle to share audio from the content on your screen. |
|
| . Whiteboard content will share automatically. |
Tap Stop presenting or Stop sharing when you're done.
Tip: To go forward and back in a PowerPoint presentation, swipe in the direction you'd like to go, or tap the forward and back buttons on the bottom of your screen.
Note: If your role changes from presenter to attendee during a meeting and you're presenting, screensharing will stop.
Zoom in to shared content
Want to get a better look at shared content?
Pinch in or out to zoom, and tap and drag to see different areas.
Note: Zoom isn't currently supported when you're sharing photos and videos.
Minimize shared content
You may want to minimize the content someone is sharing in order to better see the people in the meeting on your mobile device. Here's how:
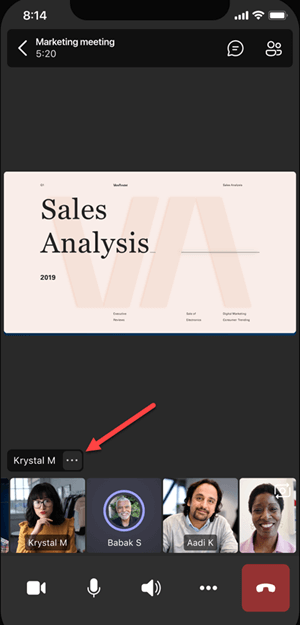
Tap Minimize content from the menu
This will give you a better look at more of the people in the meeting. You'll still see the shared content on the lower portion of your screen.

Use your phone as a companion device in a meeting
Join a meeting on more than one device for more collaboration and content-sharing options.
If you're already in a meeting on your laptop, for example, you can add your phone as a companion device to present files, share live video, and much more. Any device with the Teams mobile app can be added as a companion device—just make sure the devices you're using are signed in to the same Teams account.
There's a lot you can do when you add a companion device to your meeting experience:
Use mobile video to show things that are out of view for remote participants.
Take a photo to share with everyone or pick one from your camera roll.
Use your phone to control a presentation.
Share your mobile screen.
If you can see it on your phone, you can share it in the meeting!
Tip: For more details, see Join a Teams meeting on a second device .
Add a companion device to a meeting
Open Teams on your mobile phone when you're already in a meeting on another device.
You'll see a message near the top of your screen informing you that you're currently in a meeting on another device, and asking if you want to join it on this one, too. Tap Join .

You'll then see two options: Add this device , and Transfer to this device . Tap Add this device .
If you join this way, we'll mute your companion device's mic and speaker to avoid causing an echo effect.
When you're ready to share something from the companion device, tap Start presenting at the bottom of the screen. On your other device, you'll be able to see what you're sharing, just like everyone else in the meeting.
When you're finished, tap Stop presenting , or simply hang up. Your other device will still be connected to the meeting.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Frame your story (figure out where to start and where to end). Plan your delivery (decide whether to memorize your speech word for word or develop bullet points and then rehearse it—over and ...
4. Create audience-friendly slides and visual aids. As you start to craft your presentation, think about whether or not your audience can actually interact with your visuals. For example, if you are using slides, then they need to be visible, clear, and easily readable. Use a large font and clear lettering.
Tip #1: Tell stories. Sharing an anecdote from your life can improve your credibility and increase your relatability. And when an audience relates to you, they're more likely to feel connected to who you are as a person and encouraged to give you their full attention, as they would want others to do the same.
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation. Summary. Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or ...
Do not leave important questions unanswered at the end of the presentation. Open issues should be explicitly addressed (e.g., future work) Provide a summary of the main message of your presentation. Try to close the circle: link the results at the end to the motivating questions at the beginning.
1 Make a provocative statement. "I want to discuss with you this afternoonwhy you're going to fail to have a great career." One surefire way to get your audience's attention is to make a provocative statement that creates interest and a keen desire to know more about what you have to say. The presentation above, for example, does just that by ...
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
Ways to give an effective seminar about your research project. Grab your audience's attention by using slides as a roadmap and focusing on your role as a presenter, recommends Ananya Sen. By ...
Tip #4: Practice. Practice. Practice. You should always practice your presentation in full before you deliver it. You might feel silly delivering your presentation to your cat or your toddler, but you need to do it and do it again. You need to practice to ensure that your presentation fits within the time parameters.
Discipline. You have (or will have) an elevator pitch from the job market - use this to trim your presentation. A few bonus resources from others Marc Bellemare has a great series of "22 tips for conference and seminar presentations," many of which apply to short presentations: "Always provide a preview of your results. This isn't a ...
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation. First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Though this does not mean that a 75-minute seminar needs 75 slides (most of my seminar presentations have fewer than 60 slides), it really does mean that a 15-minute conference presentation should have no more than 15 slides. What your presentation should include is really a function of time. For example, when presenting my work with Tara ...
Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it. Craft a compelling research narrative. After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story.
11 "Do's" for Giving a Great Presentation. 1. Believe that giving a great presentation is a learnable skill. Giving a good presentation is a learnable skill. Even true introverts can give excellent presentations. In fact, introverted people actually tend to plan better presentations though they may be more afraid to give them.
1. Tell your audience who you are. Start your presentation by introducing yourself. Along with sharing your name, give your audience some information about your background. Choose details that are relevant to your presentation and help establish you as an expert in your chosen topic. Example: "Good morning.
Try a story (see tip 7 below), or an attention-grabbing (but useful) image on a slide. 6. Remember the 10-20-30 Rule for Slideshows. This is a tip from Guy Kawasaki of Apple. He suggests that slideshows should: Contain no more than 10 slides; Last no more than 20 minutes; and. Use a font size of no less than 30 point.
At each "click" on your slides, new information is shown on the slides. Let's mark by (slides) the amount of information added following a "click". Let's mark by (speech) the amount of information conveyed by your speech between two "clicks". A good presentation has (slides)= (speech) at each point in the presentation.
Transition into your presentation to keep the audience's attention. Start by posing the central problem, question, or issue you're there to address with your seminar. Give a brief outline of the information you're going to cover with your presentation. This is what the attendees came to hear about, after all!
How to Give a Good Senior Seminar Presentation. 1. Pick a good topic Choose a topic that is of interest to you and of general interest as well. Remember that a seminar is really a story, and giving a good seminar is the same thing as telling a good story. Selecting a topic that will make a good story is a big first step toward making your ...
As a dynamic seminar leader, it's crucial to have a roster of stimulating and thought-provoking topics. These 200 seminar topics are designed to ignite lively discussions and enrich your upcoming sessions! The Future of Artificial Intelligence: Opportunities and Challenges. Climate Change and Sustainability Practices.
Key Takeaways: Understand your purpose for presenting, structure your presentation in a logical manner, and prepare as much as possible. Remember to breathe during your presentation! This will help keep you calm and focused. Structure your presentation with a beginning, middle, and end.
Memorize your presentation to gain even more confidence. Putting in the extra work will ease your nerves and dramatically improve your effectiveness in front of a room. How To Give A Seminar Presentation That Sells. Seminar sales won't happen spontaneously; you have to align your goals and actions to earn the sale.
CISO candidate presentation on Aug. 6. August 02, 2024. Article by IT Communication Group. UD faculty invited to lead Delaware Teachers Institute seminar. August 01, 2024. Article by Jon Cox. See More Stories
You need to share a presentation and want others to be able to move through it at their own pace. For info on PowerPoint sharing, see Share PowerPoint slides in a Teams meeting. Whiteboard. Collaborate with others in real time. You want to sketch with others and have your notes attached to the meeting.